According to data from mortgage analytics firm Optimal Blue, the average interest rate for a 30-year fixed-rate conforming mortgage loan in the United States stands at 6.808%. This marks a slight decrease of about one basis point compared to the previous business day and roughly three basis points lower than the week before. Explore the latest rates for various conventional and government-backed mortgages, analyzing whether they are trending upward or downward.
Details on Current Mortgage Rate Dynamics
In the realm of home financing, June has seen fluctuations influenced by broader economic trends. As of mid-month, the typical borrower seeking a long-term fixed-rate mortgage encounters rates hovering around 6.8%, reflecting ongoing market uncertainties. Observers note that since last September, when the Federal Reserve began adjusting the federal funds rate, there was hope for softer mortgage rates. However, this expectation did not materialize; instead, after a brief dip prior to the September meeting, rates rebounded sharply.
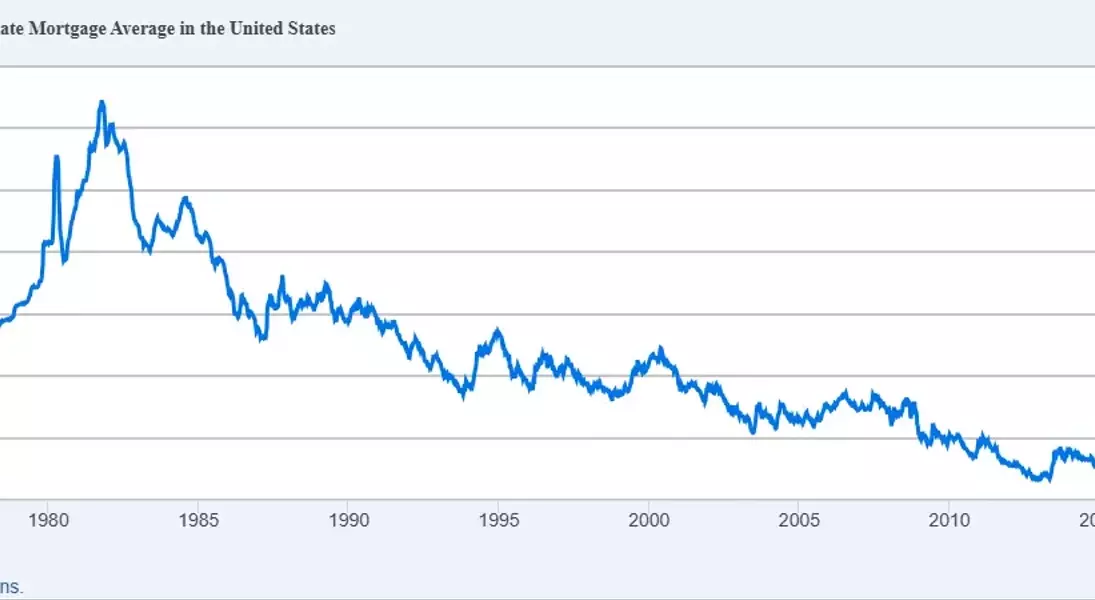
By January 2025, Freddie Mac reported that the average 30-year fixed-rate mortgage surpassed 7% for the first time since May of the previous year. This contrasts sharply with the record low of 2.65% observed in January 2021 during pandemic-driven stimulus efforts. Experts concur that barring unforeseen global calamities, mortgage rates are unlikely to return to the 2%-3% range within our lifetimes. Nevertheless, achieving rates near 6% remains plausible if inflation is controlled and lenders gain confidence in the economic outlook.
Amid these developments, potential buyers face challenges exacerbated by policy uncertainties under President Donald Trump's administration, including concerns over tariffs and immigration policies. Despite high rates, strategies exist to enhance affordability, such as negotiating rate reductions with builders for newly constructed homes.
Strategies for Securing Competitive Mortgage Rates
While macroeconomic conditions remain beyond individual control, optimizing personal financial profiles significantly impacts achievable mortgage rates. Key steps include maintaining excellent credit health, ideally aiming for scores exceeding 740, which lenders categorize as top-tier. Additionally, keeping debt-to-income ratios below 36% enhances approval prospects, although some flexibility exists up to 43%.
Engaging multiple lenders through prequalification processes fosters informed decision-making. Comparisons should account for variations like discount points, ensuring apples-to-apples evaluations. Furthermore, understanding historical contexts underscores current rates' relative normalcy compared to earlier decades, where double-digit percentages were commonplace.
Factors driving mortgage rate fluctuations encompass inflation fears, national debt levels, loan demand dynamics, and Federal Reserve actions. The latter includes both federal funds rate adjustments and balance sheet management, particularly involving mortgage-backed securities (MBS). These elements collectively shape lending environments and influence borrowers' experiences.
From a journalistic perspective, navigating today's mortgage landscape requires diligent research and strategic planning. Recognizing the interplay between economic indicators and personal finance empowers consumers to make prudent choices amidst shifting market conditions. Ultimately, staying informed equips prospective homeowners to seize opportunities while mitigating risks associated with fluctuating rates.
